Take Advantage of the Dev Container Feature in VS Code
What is a Container?
If you are familiar with container or Docker, you can skip this section.
A container is a lightweight, portable, and self-sufficient unit that can run software in an isolated environment.
It packages the application code along with its dependencies, libraries, and configuration files, ensuring that it runs consistently across different computing environments.
Containers are built on top of containerization technologies like Docker, which allow developers to create, deploy, and manage applications easily.
The term "container" is often used interchangeably with "Docker container," as Docker is the most popular containerization platform.
What is a Dev Container?
A Dev Container is a special type of container that is specifically designed for development purposes. It provides a consistent and isolated environment for developers to work in, ensuring that the application behaves the same way regardless of where it is run.
It can solve many common development issues, such as dependency conflicts, environment inconsistencies, and version mismatches. By using a Dev Container, developers can ensure that their development environment is reproducible and consistent, making it easier to collaborate with others and avoid "it works on my machine" problems.
Benefits of Using Dev Containers
Using Dev Containers in your development workflow offers several benefits:
Consistent Development Environment: Everyone on the team works with the exact same environment, eliminating "it works on my machine" problems.
Isolation: Your development environment is isolated from your local system, preventing conflicts between different projects or versions of dependencies.
Easy Onboarding: New team members can get started quickly without spending time configuring their local environment.
Reproducible Builds: The development environment is defined as code, making it reproducible across different machines.
Clean Local Machine: Keep your local machine clean as all project-specific dependencies are contained within the container.
Prerequisites for Using Dev Containers
Before you start using Dev Containers in VS Code, you need to ensure that you have the following prerequisites installed:
Docker
Dev Containers rely on Docker to create and manage container environments. You need to install Docker before using Dev Containers.
You can choose Docker Desktop (on Windows and macOS) or Docker Engine (on Linux) from Docker's official website. You can also use third-party Docker tools like OrbStack, refer to Using Docker on Silicon chip (M1/M2/M3) Mac computers for more details.
VS Code
Make sure you have the latest version of Visual Studio Code installed. You can download it from code.visualstudio.com.
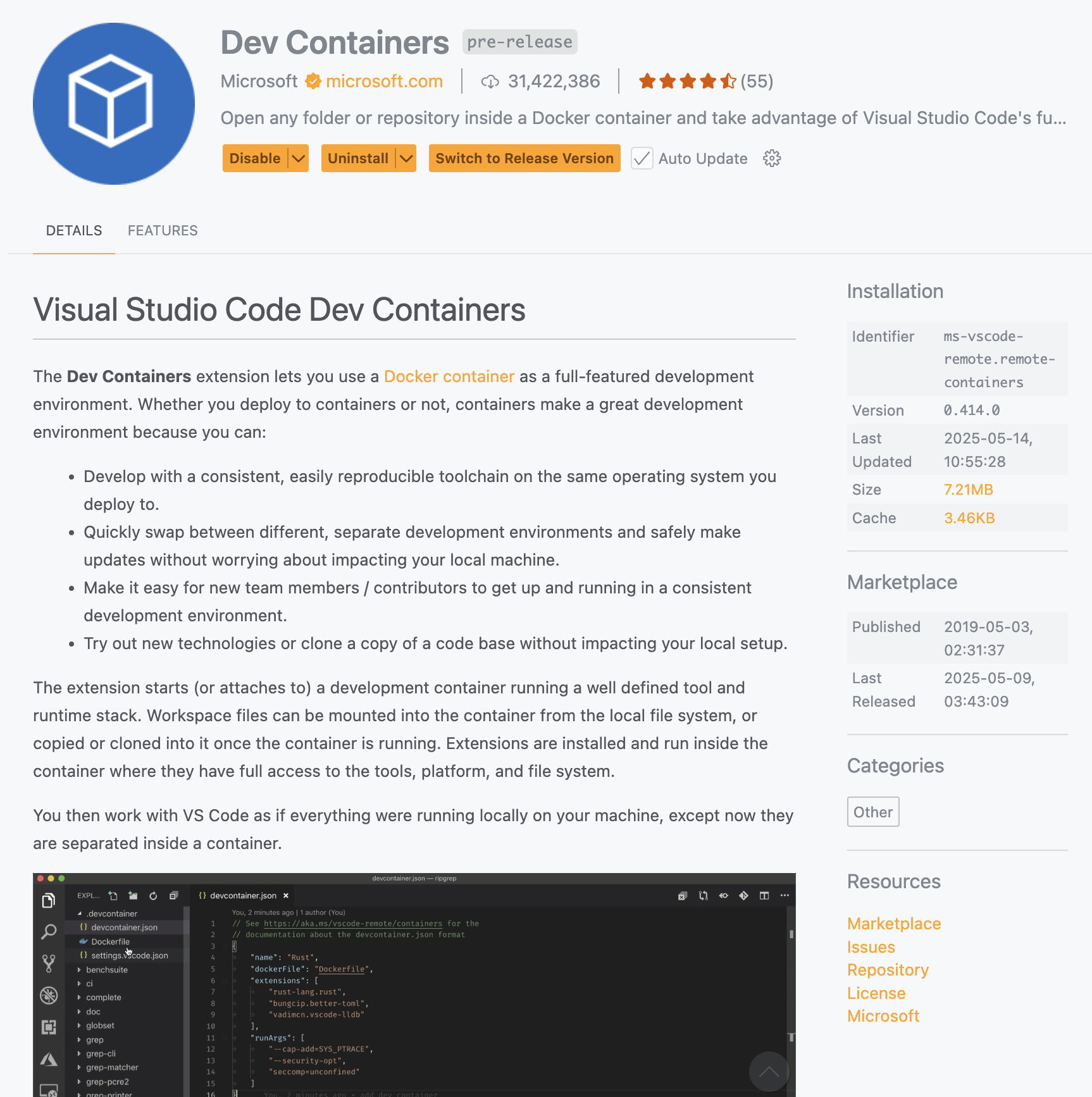
Dev Containers Extension
Install the Dev Containers extension from the VS Code Marketplace.
How to Use Dev Containers in VS Code: A Step-by-Step Guide
To use Dev Containers in Visual Studio Code, first open your project, then follow these steps:
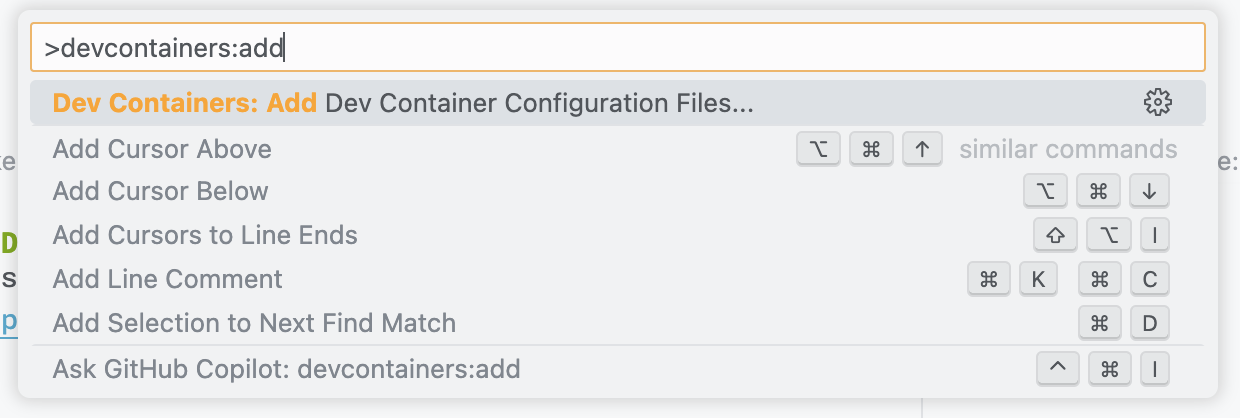
Add Dev Container Configuration:
Open the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P on macOS) and type "Dev Containers: Add Development Container Configuration Files...", then choose "Add configuration to workspace".
Select a predefined Dev Container configuration from the list. For example, select "Node.js & TypeScript" if you're working on a Node.js project.
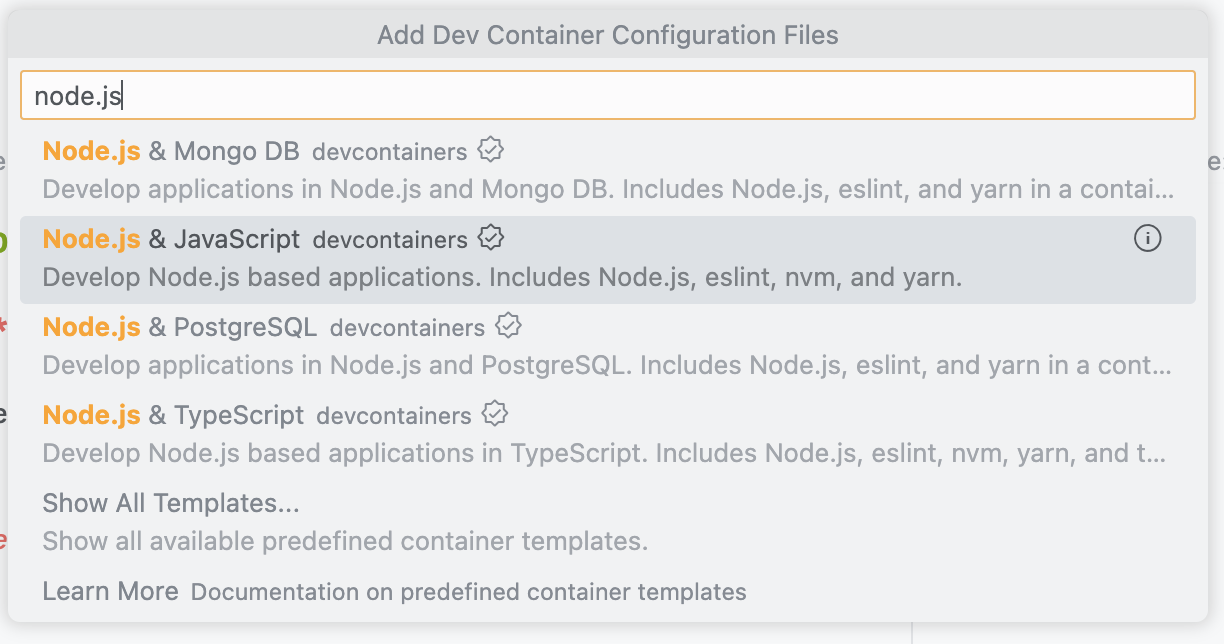
Then choose the image version & other options based on your project requirements, if you are not sure, you can go with the default options.
After that, VS Code will create a .devcontainer folder in your workspace with a config file devcontainer.json:
json
// For format details, see https://aka.ms/devcontainer.json. For config options, see the
// README at: https://github.com/devcontainers/templates/tree/main/src/javascript-node
{
"name": "Node.js",
// Or use a Dockerfile or Docker Compose file. More info: https://containers.dev/guide/dockerfile
"image": "mcr.microsoft.com/devcontainers/javascript-node:1-22-bookworm"
// Features to add to the dev container. More info: https://containers.dev/features.
// "features": {},
// Use 'forwardPorts' to make a list of ports inside the container available locally.
// "forwardPorts": [],
// Use 'postCreateCommand' to run commands after the container is created.
// "postCreateCommand": "yarn install",
// Configure tool-specific properties.
// "customizations": {},
// Uncomment to connect as root instead. More info: https://aka.ms/dev-containers-non-root.
// "remoteUser": "root"
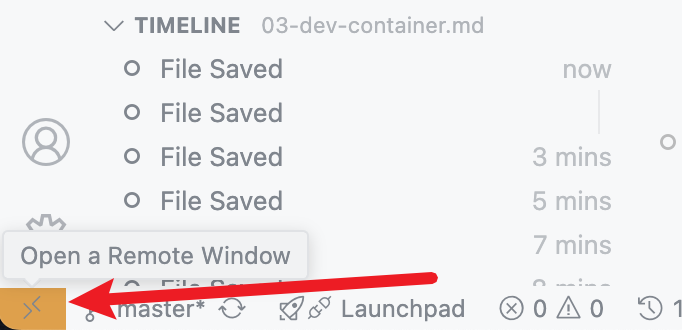
}Open Your Project in the Dev Container:
You can then open the Dev Container by clicking on the "Open a remote window" button that appears at the bottom left corner of the VS Code window, then selecting "Reopen in Container".
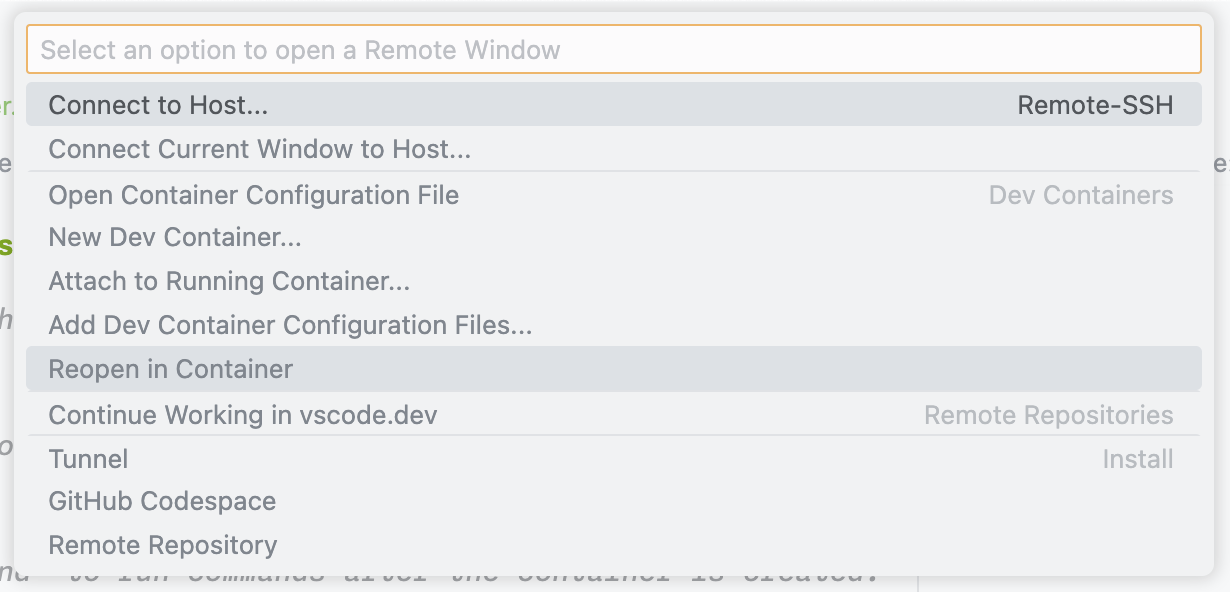
Alternatively, you can open the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P on macOS) and type "Dev Containers: Reopen in Container".
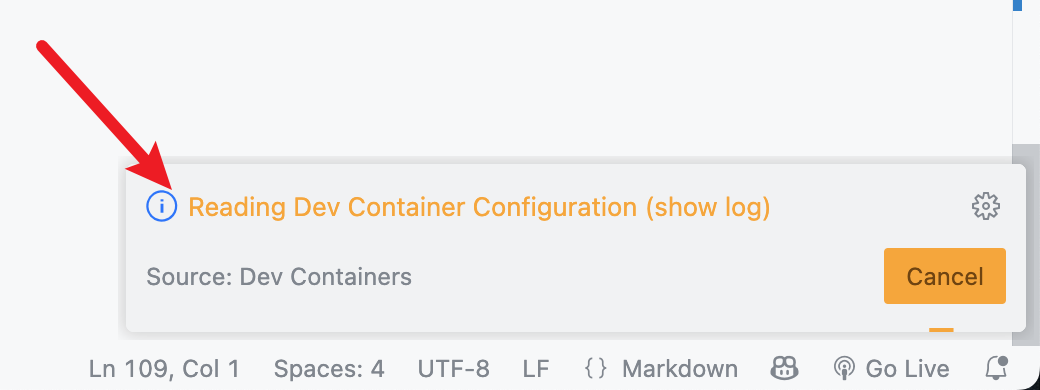
Then you will see a progress bar indicating that VS Code is building the Dev Container image and starting the container. You can click on the "Show Log" button to view the build logs.
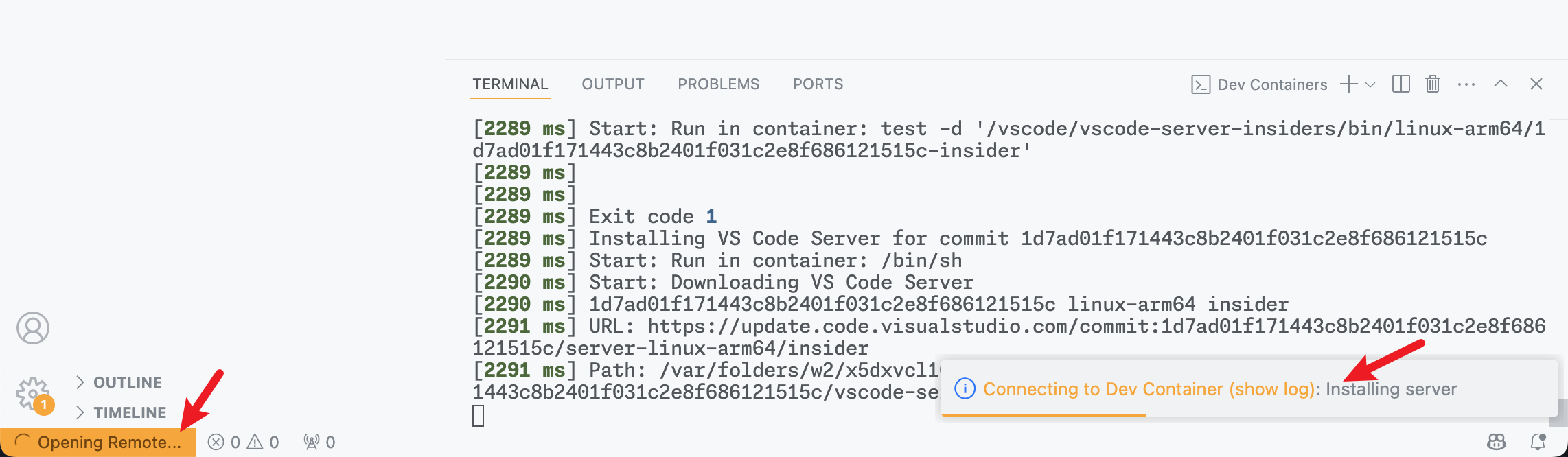
If everything goes well, you will see a new VS Code window that is connected to the Dev Container. Before you can start working, you may need to wait for the container to finish initializing (download and install necessary dependencies and extensions).
Once the container is ready, you can start working on your project inside the container.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter any issues with Dev Containers, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Docker is Running: Make sure Docker is installed and running on your machine.
- Increase Resource Allocation: If containers are running slowly, try increasing the memory and CPU allocation for Docker in the Docker Desktop settings.
- Update VS Code and Extensions: Make sure you're using the latest version of VS Code and the Dev Containers extension.
- Check Network Settings: If your container needs to access network resources, ensure firewall settings aren't blocking connections.
- Review Logs: Use the "Show Log" button in the Dev Containers progress bar to view detailed logs for troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Dev Containers in VS Code provide a powerful way to create consistent, isolated development environments. By leveraging container technology, you can ensure that your development environment is reproducible across different machines and avoid common environment-related issues.
Whether you're working on a personal project or collaborating with a team, Dev Containers can streamline your workflow and make it easier to focus on writing code rather than configuring environments.
